People with geographic tongue have smooth, reddish patches surrounded by white borders on their tongues. It’s a harmless, non-contagious condition. However, if you feel pain or discomfort on your tongue, take pain relievers and avoid the foods that trigger the pain.
What is geographic tongue?
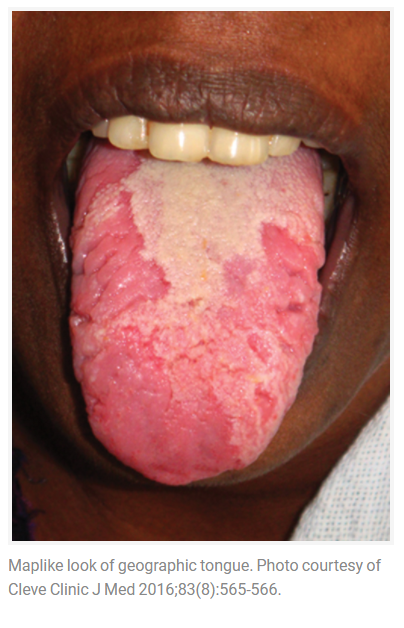
Geographic tongue is a condition that causes a map-like pattern to appear on the tongue. People with this condition have smooth, reddish patches surrounded by white borders on their tongues. The red areas are missing the tiny bumps (papillae) that naturally appear on the surface of the tongue.
Geographic tongue is benign (harmless) and does not cause any long-term health problems. It is not contagious. Most people have no symptoms, but some people feel a burning or stinging sensation on their tongue. Treatment for geographic tongue usually isn’t necessary.
How common is geographic tongue?
Doctors aren’t sure how many people have geographic tongue. Some doctors estimate that about 3% of the population has the condition, but it may occur more frequently.
Who is affected by geographic tongue?
Geographic tongue (also called benign migratory glossitis) is slightly more common in young adults, though doctors aren’t sure why. People who have psoriasis (a condition that causes scaly patches on the skin) and reactive arthritis (Reiter’s syndrome) are more likely than others to have geographic tongue. The condition appears in people of all ages, including babies and children.
How do people get geographic tongue?
Doctors aren’t sure what causes geographic tongue, but they do know that it is not contagious. Because it often runs in families, doctors believe it may be inherited (passed down) from parents to their children.
People commonly have other conditions along with geographic tongue. These conditions and diseases include:
- Psoriasis: Many people with geographic tongue also have psoriasis, an inflammatory skin condition.
- Hormonal surges: Women who are taking oral contraceptives (birth control pills) have developed geographic tongue, possibly due to the female hormones in the pills.
- Vitamin deficiencies: People who don’t have enough zinc, iron, folic acid and vitamins B6 and B12 are more likely to have geographic tongue.
- Fissured tongue: Doctors think there might be a genetic link between geographic tongue and fissured tongue, a condition that causes deep grooves or wrinkles on the tongue.
- Diabetes: Some doctors have found that people with diabetes, especially type 1 diabetes, have a higher chance of developing geographic tongue.
- Allergies: People with eczema, hay fever and other allergies may have an increased chance of having the condition.
- Emotional stress: Doctors have found a link between increased stress and geographic tongue.
What are the symptoms of geographic tongue?
While many people don’t notice any symptoms at all, the most recognizable sign of geographic tongue is the appearance of the pattern on the tongue. Symptoms can come and go, and may last a few weeks or years. They include:
- Red spots on the tongue: The red patches on the tongue appear in an irregular map-like pattern and are often surrounded by white or gray borders. They appear anywhere on the top, sides and tip of the tongue. The patches may come and go, and can change size, shape and location over time.
- Absence of papillae: The insides of the red patches are noticeably smoother because they do not have any papillae. Papillae are tiny bumps that coat and protect the entire tongue and help us chew food. Some papillae also have taste buds.
- Burning sensation: Some people with geographic tongue feel a stinging, tingling or burning sensation on their tongue, especially when eating. Discomfort is usually mild and can come and go along with the red patches.
- Patches in other areas of the mouth: Occasionally, similar red patches can form on the gums, the top of the mouth or inside the cheeks. These patches are called geographic stomatitis or erythema migrans. The patches are not the same as the erythema migrans rash that appears in the early stages of Lyme disease. Having these patches in your mouth does not mean that you have Lyme disease.
How is geographic tongue diagnosed?
Doctors diagnose geographic tongue with a physical exam. Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, including any discomfort while eating or drinking.
How do I know if I have geographic tongue?
If you have tongue pain and smooth, red spots on your tongue in a map-like pattern, you could have geographic tongue. While geographic tongue is harmless, you should see your doctor to rule out other medical conditions.
What are the treatments for geographic tongue?
Because geographic tongue is a benign condition, treatment is not necessary. If you feel pain or discomfort, you should avoid eating anything that can irritate your tongue, such as spicy food. To relieve the stinging or burning sensation, your doctor may recommend:
- Mouthwash with an antihistamine (medication to relieve allergic reaction).
- Topical analgesics (pain relievers) that you can apply directly to your tongue.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
What are the side effects of the treatment for geographic tongue?
Side effects from NSAIDs are rare, but they can occur. They usually only appear after someone has taken a medication for a long time. Side effects of NSAIDs can include:
- Stomach pain and heartburn.
- Stomach ulcers.
- Headaches and lightheadedness.
- High blood pressure (hypertension).
What are the complications associated with geographic tongue?
Geographic tongue is a harmless condition with no long-term health complications.
What can I do to help relieve symptoms of geographic tongue?
To relieve the stinging and burning sensation, you should avoid eating or drinking anything that can irritate your tongue, such as hot or spicy food. You should also avoid chewing tobacco since it can make the pain and stinging worse.
What is the outlook for patients who have geographic tongue?
Geographic tongue is harmless. Most people who have geographic tongue have mild symptoms or no symptoms at all. A small group of people have recurring pain and discomfort on their tongue. They manage it with pain relievers and by avoiding foods that trigger the pain.
When should I call my doctor about geographic tongue?
If you have symptoms of geographic tongue, you should visit your doctor to rule out other medical conditions. A red, swollen, or sore tongue could be a sign of another medical problem, so it’s important to see your doctor.
Source:


